The Contact ID protocol from Ademco is a respected digital communication format that has been in use for several years by most security companies to link security alarm systems with their Central Monitoring Stations (CMS) or Alarm Receiving Centers (ARC).
Roombanker’s home security hub support both Contact ID and SIA DC 09 protocol to communicate with ARC/CMS. We will later introduce our successful cases using Contact ID protocol to simplify our system integration with security alarm providers.
Here’s how this protocol works and why you should partner with us to deploy this product in your intruder/burglar alarm systems.
What is the Contact ID Protocol?
The Ademco Contact ID protocol is one of the most commonly used security alarm system protocols to facilitate communication between homes and ARC/CMS. This protocol is a communication format that uses 16 digits to send information from the alarm system, the home security hub in this case, and the central station (ARC or CMS).
Contact ID uses DTMF to send the alarm signal or message over phone lines, and it can send the 16-digit message within milliseconds.
How Does Contact ID Protocol Work in an Alarm System?
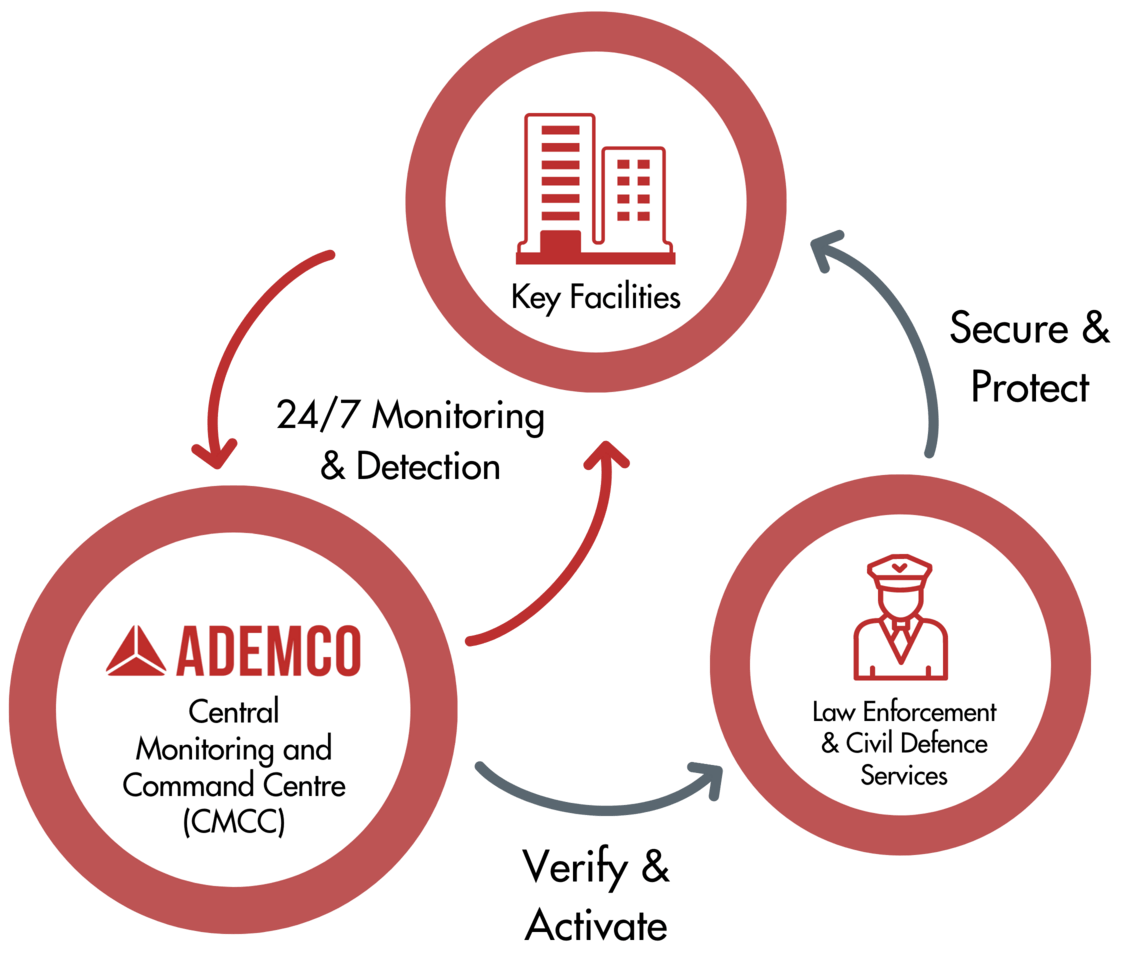
When the home security system’s sensors trigger an alarm due to intrusion, the hub kickstarts this communication sequence with the ARC or CMS.
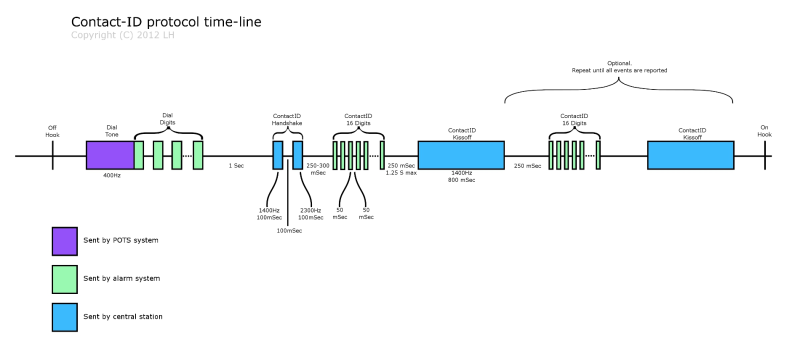
- The hub dials the alarm receiving center’s telephone number.
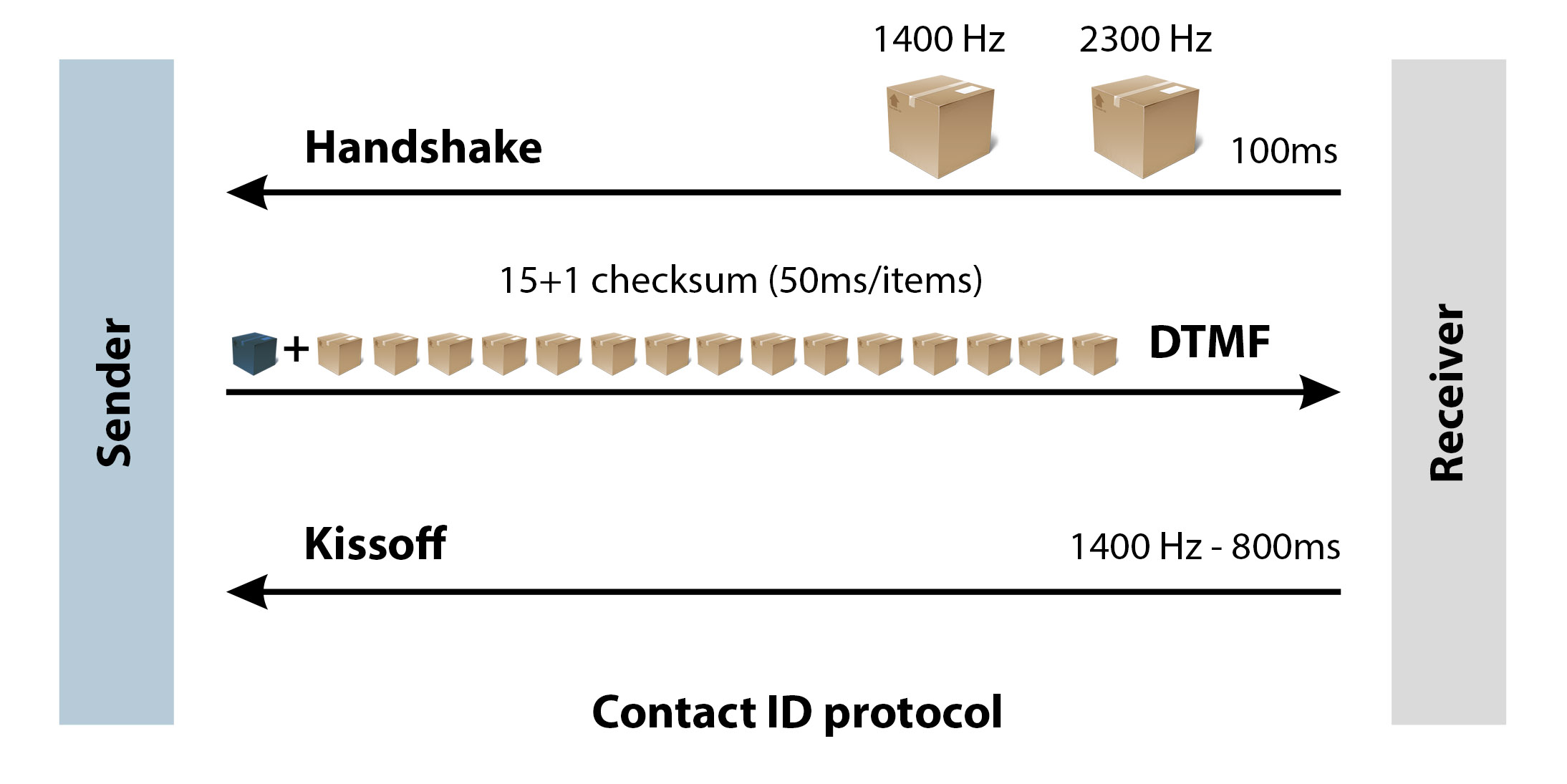
- Once the receiving center responds, it sends a handshake signal back to the hub to confirm it is listening. This handshake signal has the format of a 1400 Hz pure tone pulse that lasts for 100 ms followed by 100 ms of silence, and then 100 ms of a 2300 Hz pure tone pulse.
- On receiving this handshake, the hub waits for 250 ms, then sends the Contact ID message, which contains 16 DTMF digits to the receiving center. Each digit is 50 ms long and is separated from the next one using 50 ms of silence.
- After sending the entire message, the receiving center verifies its correctness using the last check-sum digit. After verification, it sends a confirmation or Kissoff signal back to the hub to disconnect. This signal lasts 800 ms and is a 1400 Hz pure tone pulse.
- When the hub receives this signal, it disconnects the call and the alarm message transmission is complete. But if the alarm system (hub) doesn’t receive this Kissoff signal on time, it retransmits the 16-digit message and waits for it again.
Ademco Contact ID Codes
The 16-digit Contact ID DTMF code is split into 7 parts to carry different elements of the alarm message being transmitted. These parts are:
- Account Number (0–3): Also known as user code, these first four digits represent the code for each alarm user or customer of the central station (receiving center). Ranging from 0–9999, this number informs the station of the call’s origin from the thousands of customers that have subscribed to their security service.
- Message Type (4–5): These next two numbers indicate the message type, which is always 18 for security alarm systems.
- Event Qualifier (6): The event qualification code shows the type of the event, which can be: opening (new event), closing (new restore), or status report. These are denoted by 1, 3, and 6, respectively.
- Event Code (7–9): Event codes indicate the issue that triggered the event, which can be a fire alarm, burglary, medical, panic alarm, etc.
- Group/Partition System Number (10–11): These two digits range from 01–09 and indicate whether specific group or partition information applies.
- Zone Number/Code (12–14): Zone codes show the number of the zone that triggered the alarm.
- Checksum (15): This control value helps to determine if the 15 received values are correct.
The calculation method for this checksum value is rather complicated, but it follows these steps.
- The 15-digit message codes (account number to zone code) from the alarm system are accumulated in binary numbers. If a bit of this data is zero, it is added as a binary number 0AH.
- This accumulated sum is divided by 15.
- The integer digit of the quotient is added by 1 and then multiplied by 15.
- The difference after subtracting the accumulated sum from this product is the check code.
The alarm system does this calculation to get and fit in the checksum before sending the DTMF codes, and the ARC or CMS does the same to see if the numbers match before sending the Kissoff signal.
How to Connect a Roombanker Hub to an ARC/CMS Using the Contact ID Protocol?
Roombanker’s home security hub can connect with the ARC or CMS in three ways:
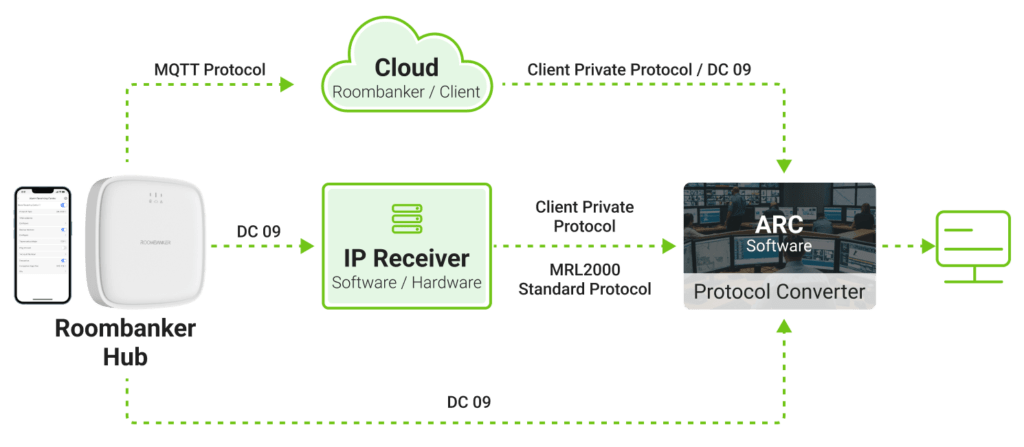
Cloud Connection
In this configuration, the hub sends the alarm notification to the security provider’s cloud server using a simple messaging protocol, such as MQTT. The server then converts this message into a language the ARC can understand, a 16-digit Contact ID DTMF code in this case, and then sends it.
Via an IP Receiver
An IP receiver is a translator or protocol converter that can understand DC 09 and Contact ID. It sits between the two sides to receive data from the Roombanker hub and dial the receiving center’s number to exchange data in Contact ID format.
Directly
Instead of having a separate protocol converter, the ARC can have an integrated interpreter, which makes it possible to send messages directly from the hub using DC 09. The built-in converter translates the data to enable each the ARC software to understand and respond accordingly.
Roombanker is Looking For Intruder/Burglar Alarm Partners
If your customers are looking for a professionally-monitoring wireless security alarm system, we can partner to help you provide them with stylish, design-forward, affordable, and most importantly, compatible technology that operates seamlessly.
In the case of burglar or intruder alarm systems communicating using Contact ID, the challenge comes in integration because modern systems are shifting to SIA (DC 09). But Contact ID is still popular and some applications might be better served using this protocol, so we provide this option to help you cover more customers.
In addition to providing ARCs with robust and reliable communication infrastructure using industry-standard protocols (SIA and Contact ID codes), Roombanker offers flexible solutions that can transmit the 16-digit message using phone (VoIP) or SMS to suit your preference.
But we don’t limit our partnership to these options. We understand that ARCs have unique needs, so we can tailor the solution to suit your requirements and make it fit into your existing ARC infrastructure. Contact us to discuss your requirements in detail so that we can determine the best way forward.

FAQs on Ademco Contact ID Protocols
Why Use Alarm Protocol Between Home Security System and ARC/CMS?
Alarm protocols provide safety and security when exchanging data from the home security system and ARC/CMS. They simplify call handling as well because the message contains all the relevant information that determines the most suitable response action to take.
What’s The Origin of the Contact ID Protocol?
Ademco introduced the Contact ID protocol in the 1980s, which used DTMF to send a ton of information from complex alarm systems in a few seconds. The company was one of the largest providers of security and fire protection solutions and services at the time, and it made both receivers and alarm panels of different sizes that communicated quickly and reliably.
Being the leader in this field meant the company provided market standards. Therefore, Contact ID became a major alarm protocol because almost all other panel and receiver makers implemented this communication format in the 80s, 90s, and even to date.
Later on, the SIA (Security Industry Association) formalized the protocol and published it as DC 05 to enable panel and receiver makers to follow similar event codes and digit timing.
What Is DTMF?
Also known as touch-tone signaling, DTMF (Dual Tone Multi-Frequency) is a standard signaling method for phone dialing and data transmission that uses two sine waves at different frequencies to communicate. Bell Systems introduced DTMF in 1963 as a quicker way to send alarm signals via phone lines.
The name “touch-tone” comes from the sound phone buttons make when pushed down. Each button emits two tones when pressed, each producing sound at two different frequencies that the central station receiver can decode and interpret.
DTMF enabled automation for alarm communication, leading to the birth of protocols like Contact ID.
What Is the Difference Between SIA and Contact ID?
SIA is more of a standardization organization that publishes the acceptable protocols for communication between on-premise security alarm systems and a central station. These standards change over time as user, data security, and other demands change over time.
For instance, SIA published Ademco’s Contact ID as DC 05 back in 1999 because it was the best at the time. But the current published standard (DC 09) is better in terms of encryption and messaging. It’s similar to how standards like ISO change and improve over time.
