Detecting water leaks is an important part of modern home automation and security systems equipment. Apart from Home automation, it is widely used in commercial automation and protection of server rooms, data centers, pantries, and plumbing systems.
As technology advances, the question arises: what wireless protocols should be incorporated for IoT-based water leakage? In this article, LoRa technology will be described, and you will be introduced to a rather promising counterpart of this technology – RBF.

What is a LoRaWAN Water Leak Detector?
Water leak detectors are current LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) systems that are IoT devices that make use of sensors to detect the existence of water where it is not wanted. These devices operate on LoRaWAN a low-power, wide-area networking LPWAN system which is suitable for battery-operated wireless devices in a regional, national, or global LPWAN network.
LoRaWAN leak detectors typically consist of three main components:
- The sensor body: This houses the main circuitry and battery.
- A cable: This connects the sensor body to the probe.
- The probe: Often features two contact points for more accurate detection.
Whenever water touches the probe it makes an electrical circuit and there is an alarm. LoRaWAN technology then enables the provision of this alert over long-range to the central smart hub from where it can transfer the information to the user’s smartphone or a control panel.
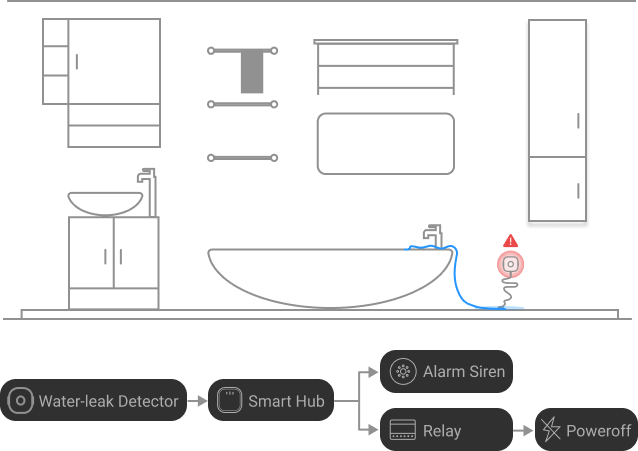
Why Use LoRaWAN or Similar Technology?
The adoption of LoRaWAN and similar technologies for water leak detection offers several significant advantages:
- Exceptional Range: LoRaWAN devices can send data up to 1-10 Km away, and this is completely sufficient for homes or even big commercial facilities.
- Superior Penetration: LoRaWAN operates in the low-frequency bands and therefore its signals can easily go through the walls, floors or any other structure as compared to frequencies used of Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
- Extended Battery Life: Thus, a LoRaWAN water leak detector can function for up to two years or more with a single battery due to its low-power mode.
- Scalability: LoRaWAN networks can accommodate thousands of devices; therefore, they are perfect for massive integration in smart cities or big industrial zones.
- Cost-Effective: LoRaWAN devices have longer-range capabilities with less power consumption which can decrease the cost of infrastructure for WAMS applications.
- For such a case of a water leak detection system based on IoT using LoRaWAN, these features could be considered as the strengths of the technique.
What is RBF? Similarities and Differences Between RBF and LoRa Technology
Though the IoT community has warmly embraced LoRaWAN, another technology known as RBF is also eyeing water leak detection and other smart home applications. Let’s explore the similarities and differences between these two technologies:
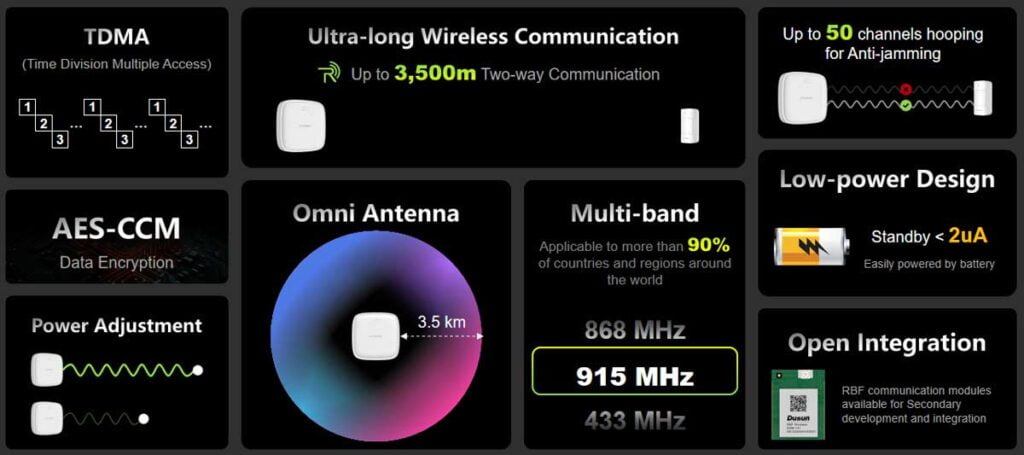
Long Range Capabilities
Both LoRa and RBF are designed for long-range communication, but there are some differences in their reach:
- LoRa: It can extend up to 1-10 kilometers, in this sense it is perfectly suitable for very large-scale applications.
- RBF: Provides up to 3 in the offer. 5 kilometers, which is enough for apartments, small businesses, and villa houses distance is more than enough.
Thus, even though the maximal range of LoRa is slightly higher than that of RBF, the latter is more suitable for the markets targeted by the company that developed it – residential and small commercial.

Anti-Interference Properties
Both technologies operate in the sub-GHz frequency band, which provides excellent anti-interference capabilities:
- LoRa: Employ a spread spectrum modulation which increases its resistance to interference.
- RBF: Also uses sub-GHz frequencies to keep the signal clear despite of interference from other appliances.
This shared characteristic guarantees that both LoRa and RBF devices can easily have favorable communication with one another regardless of the electromagnetic interference of their immediate environment.
Power Consumption
Low power consumption is a critical factor for battery-operated devices like water leak sensors:
- LoRa: Offers extremely low power consumption, with a standby current of approximately 2μA.
- RBF: Boasts even lower power consumption, with a standby current of less than 2μA.
RBF is just a tad more energy efficient and could therefore extend battery time by a small bit although both are power efficient.
Data Speed
While water leak sensors don’t typically require high data rates, the speed capabilities of each technology can impact overall system responsiveness:
- LoRa: Provides data rates that start from 0. 3 to 50 kbps.
- RBF: Offers more number of speeds starting from 2 kbps up to 1 Mbps.
Higher maximum data rate of RBF might be beneficial in conditions that demand extra sensor information or more often updates.
Ecosystem and Adoption
- LoRa: Has a well-established ecosystem with widespread adoption across various IoT applications.
- RBF: A newer technology with a growing ecosystem, particularly strong in smart home and small business applications.
While LoRa has the advantage of broader market adoption, RBF is positioning itself as a specialized solution for residential and light commercial use cases.
Also read: Why Wireless Security Alarm Devices Prefer Proprietary Protocols?
How Does an IoT-Based Water Leak Detector Work at Home?
Among the more common and also rather expensive issues for the owners of houses and apartments are water leakage. IoT-based water leak detectors are therefore sophisticated solutions to this age-old problem irrespective of the underlying technology being LoRaWAN or RBF. Here’s how these systems typically function in a home environment:
- Sensor Placement: Water leak sensors are strategically placed in areas prone to leaks, such as:
- Near water heaters
- Under sinks
- Around toilets
- Near washing machines and dishwashers
- In basements or crawl spaces
- Near air conditioning units or other HVAC equipment
- Continuous Monitoring: Through probes or electrodes the sensors are always able to detect whether there is the presence of water.
- Leak Detection: If the moisture is present then it connects the probes of the sensor and then alarms.
- Wireless Transmission: This alerts the central hub or gateway, which could be by use of LoRaWAN or RBF wireless network.
- Alert Notification: Some of the types of alerts include the gateway forwarding the alert to the smartphone app of the user or a master control panel. Some systems may also cause local alarms or sirens to sound.
- Remote Action: More complex systems may also enable the user to turn off the main water supply from their device to avoid water seeping into the rooms.
- Integration with Smart Home Systems: Most IoT-based water leak detectors can interface with other smart home systems, and can respond to them, and also provide more comprehensive reports.
Some of the notable benefits of the use of Internet of things-based system include; offering timely alarms and allowing for monitoring and even controlling the systems from a distance. This capability enables the water problem to be addressed promptly, and this can go a long way in preventing further damage especially if the homeowners are not around.

Structure of IoT-Based Water Leak Detectors
While designs may vary between manufacturers and models, most IoT-based water leak detectors share a common structure consisting of three main components:
1. Sensor Body:
- Marries the main circuit board and battery
- Houses the wireless communication module (LoRa module or RBF module)
- Sometimes also features LED lights for status indication.
2. Cable:
- Joints the body of the sensor to the probe for sensing water
- It enables the subject to be probed in different areas with relatively more ease.
- It is noteworthy that the length of a given forensic document can be different, depending on a model and the area of its usage.
3. Probe:
- Typically it has at least two or more contact points to ensure that currents induced are correct for water.
- These are designed to be corrosion-resistant materials for the equipment to last longer.
- Based on the above explanation, some models might contain several probes in order to be more inclusive.
This design provides flexibility concerning the installation location and the dependable identification of the NFC tag. The fact that the sensor’s body is connected with the probe via a cable implies that the main unit can be kept in dry and easily accessible rooms while the probe is placed in areas likely to develop leaks.
Typical Applications of IoT-Based Water Leak Detectors
Smart water leak detectors through IoT are used in different facets of human life in homes, offices among other places. In homes, they are usually fixed in the kitchen, bathroom and laundry, areas where gadgets that use water, such as washing machines and refrigerators, are located. They seal off areas to avoid any seepage from the sink, toilet, washing machine, or water heater thus avoiding any dampness on cabinets, floor, and other accessories around such areas.
Apart from specific appliances, these sensors are important in monitoring the plumbing systems in structures including the following. They can be installed near main water points or in mechanical rooms to give prior notice of major barring in the plumbing system. They protect against leakage coming from AC units, heat pumps, as well as boilers according to HVAC usage.
Water leak detectors in commercial premises are thus very much required to help safeguard key infrastructure. They are applied in data centers and server rooms to protect costly IT equipment from the threat of water harm. They are also useful in tracking the state of roofs and basements in as they help identify leakage due to roof damages or water ingress from the basement.
Other applications in use are used in refrigerators, ice makers as well as swimming pool equipment. These devices as real-time alerts and as part of larger smart home or building management systems act as imperative watches against water-related harm in a multitude of applications and thus help in the efficient usage of water as well as preserving the physical structures.
Also read: water leak detection in apartment
Roombanker’s Low-Power Long-Range Water Leak Detector
Another manufacturer of IoT devices that seems to provide a fairly strong opponent to LoRaWAN-based water leak detectors is Roombanker with their RBF technology. Low-power and long-range leak detection water leak detectors are intended for residential and light commercial utilities.
Key features of Roombanker’s water leak detector include:
- RBF Wireless Technology: Making use of the Company’s patented Related Body Functioning protocol that facilitates low-power communication across a long range.
- Extended Battery Life: These devices have an extremely low power dissipation of less than 2 micro Ampere and what it means is that these devices will survive for many years on a single battery.
- Adequate Range: Regarding to LoRa the maximal range is not reached, but the 3. It is too bulky for normal homes and small offices because even the signals that need a 5km transmission distance can comfortably fit into this small device.
- Faster Data Speeds: It is not required to be included in the present design of PLMN; however, it can enable up to 1 Mbps of data if it wishes to include more data-promoting applications.
- Integration Capability: Amid these sensors, it should be noted that all of them can be easily integrated into other Smart Home or Smart Building management systems.
- Temperature and Humidity Monitoring: At the moment, in their pipeline for the next product line, Roombanker aims to integrate the best temperature and humidity sensors into their water leak detectors as environment sensing is one of the primary massive emerging trends out there at the moment.
Actually, Roombanker is actively looking for distributors for Internet of Things hubs and sensors some of which are water leak detectors. It offers manufacturing solutions and more changes to the additional functions of environmental monitoring may also be incorporated into the product.

