Smart home products which are wireless types are many in the market and there are various factors that anyone in need of these products should take into consideration. One strategic area is related to the standard of interaction with smart home systems.
If it maps out the battery life that can last as long as, the distance at which smart home devices can communicate with each other, and if this communication will be encrypted as well as stable on its signal performance.
Based on the analysis of the mainstream smart home protocols in 2024, this article will also do a comparison between each smart home protocol and then finally give some tips on choosing the right smart home protocol.
In today’s smart home systems, a smart home protocol will play an important role in guiding the evolution of a complete smart home system, whether it’s at the beginning stage or being expanded.
What is Smart Home Protocol?
Smart home protocols can therefore be described as a standard and or a set of regulations that facilitate communication between devices within a smart home setting. This provides knowledge about how devices communicate, the flow through which information is exchanged, the format of the information, and the level of security implemented in the communication process.
Smart home protocols can be wired or wireless, and the majority of the systems used at the moment are wireless, as it is more convenient to put them in operation.
The protocols for smart homes are numerous, each with specific benefits and drawbacks. While some emphasize the ability to travel long distances, others stress on power usage, and still others provide bigger bandwidth for applications that require heavy usage or transmission of data. According to these criteria, the correct protocol for implementing a smart home shall be chosen depending on the types of devices to be installed.

10 Popular Smart Home Protocols in 2024
OEM or ODM Wireless Smart Home Devices
Using the following protocols to design and manufacture smart home devices is our specialty. Feel free to ask for more details!
Z-Wave
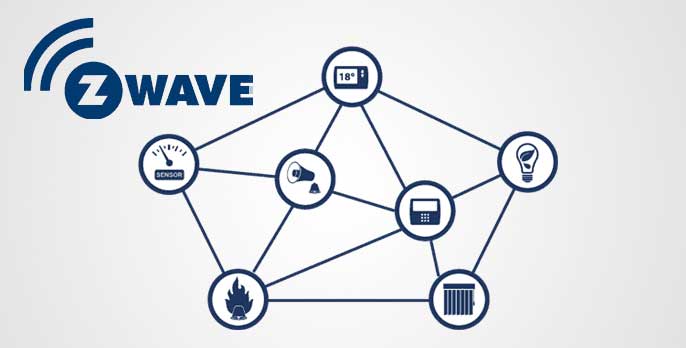
Z-Wave is a low-power, mesh network protocol that operates in the sub-GHz frequency range. This Radio has great transmission capabilities, constructive communication, and a moderately satisfactory ability to penetrate through walls. Z-Wave is fully compatible with other Z-Wave modules and systems; there are over 3,000 devices from different manufacturers.
The most cited strength of Z-Wave is that the whole system can be constructed as a mesh network where the nodes not only function as communicating devices but also as repeaters. This makes Z-Wave suitable for use in large houses or places with many corners and, therefore, many directions.
Zigbee
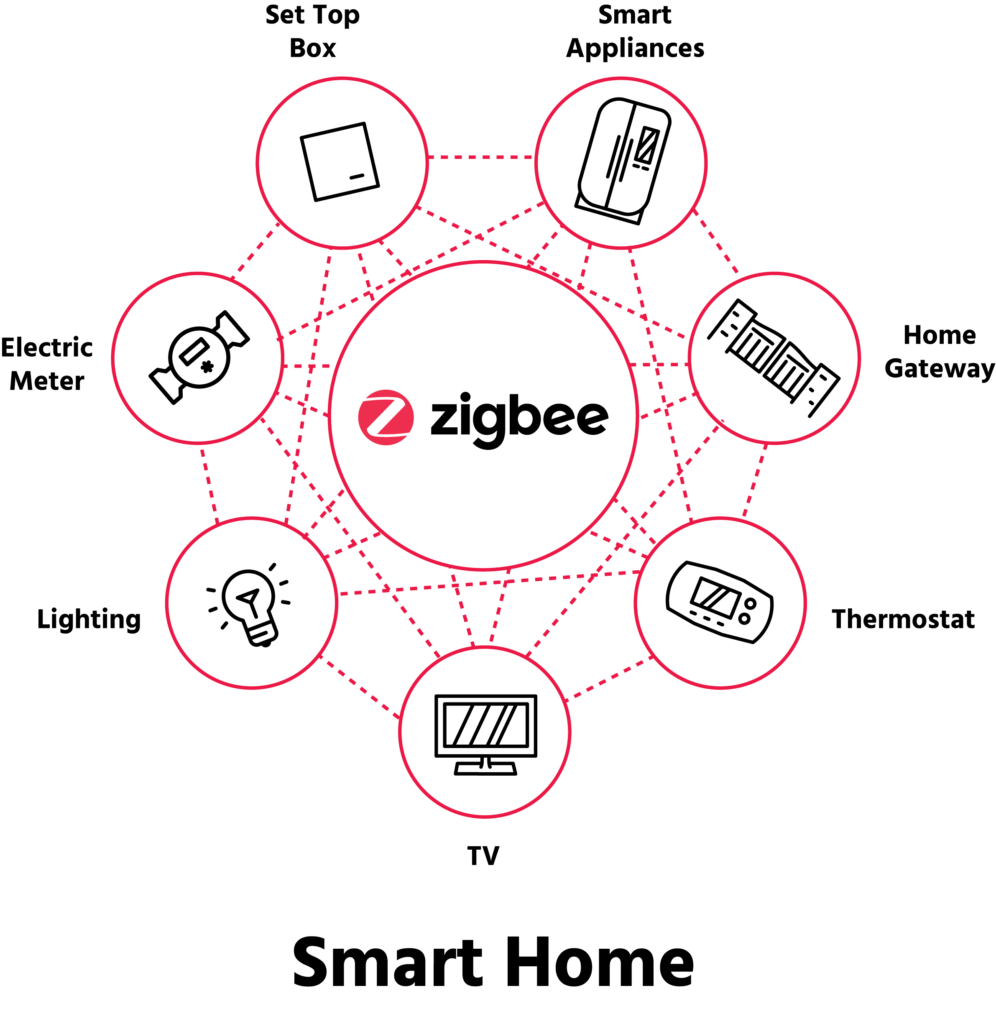
Zigbee is another low-power, mesh network protocol that operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Conclusively, it retains the support of many nodes and provides fair range as well as power consumption. It is quite popular in smart homes, where it is used with everything from lights to sensors and much more.
Mesh networking present in Zigbee enables the devices installed to pass information, and multiple devices can be connected; some can be connected directly to the hub while others will have to rely on the other devices which are in close contact with the hub. This helps to ensure that the position of the network continues to be secure and optimum all through the actual increase in the number of devices.
Matter
Matter is a relatively new protocol that has gained significant popularity in 2024. Developed by the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA), Matter aims to unify the smart home ecosystem by providing a single, secure, and reliable protocol for devices from different manufacturers.
Another advantage of Matter for smart home devices is that this implementation consumes more energies from their pros but focuses on the interoperability among them. Lastly, due to Matter’s availability, a unified smart home system can be established easily and without complications when integrating devices from different brands.
RBF
RBF (Roombanker Frame) is a proprietary protocol developed by Roombanker. It is designed for low-power, long-range communication up to 3500 in open area. RBF is optimized for smart home applications and offers advanced security features.
Roombanker’s RBF protocol is particularly well-suited for large homes or those with thick walls, as it offers excellent range and wall penetration capabilities. The protocol’s advanced security features ensure that communication between devices remains private and secure.

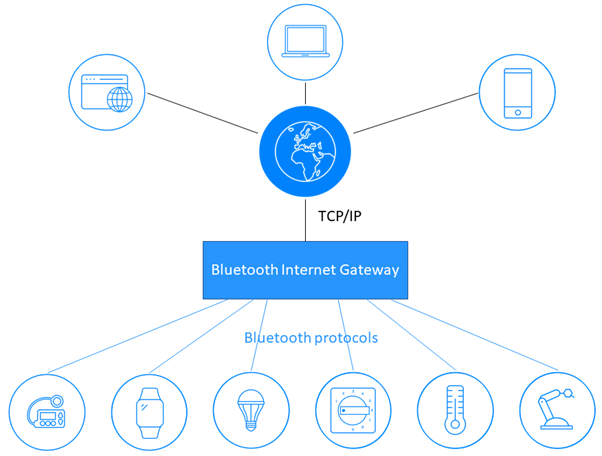
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless protocol that is particularly well-suited for wearables and home health monitoring devices. It offers low power consumption and short-range communication, making it ideal for devices that need to be worn or carried around.
Low power consumption is characteristic of BLE’s which extends the utilization hours of Battery charged device. This holds true, especially for wearables and other gadgets that require to be used round the clock for various functions.
Sub-GHz protocols
Sub-GHz protocols, such as those operating in the 433 MHz or 868 MHz frequency bands, offer long-range communication and good wall penetration. They are often used for outdoor smart home devices or those that need to cover large areas.
As noted earlier, sub-GHz protocols are characterized by the capability of long-range communication while consuming very little power. This makes them ideal for use in battery-operated gadgets that must function in areas that cannot be reached by power lines or in harsh settings.
LoRa
LoRa is a long-range, low-power protocol that operates in the sub-GHz frequency range. It is excellent for use in smart home devices as it has a wide range and low power, especially when needed to transmit data over long distances or in interfering surroundings.
Smart home applications are also a great use case for LoRa’s long-range connectivity as it is desirable for the devices to communicate with a main controller or a gateway from a significant distance. This is especially helpful for the devices that are fixed to areas that can hardly be accessed like doors and fencing sensors.
Wi-Fi
Of the wireless protocols that are available today, Wi-Fi is the most used one that provides high bandwidth, and wide coverage. Video doorbells, security cameras, or streaming devices that generate data demands are especially suitable for a smart home. They are known to have poor power efficiency as compared to other protocols in regards to Wi-Fi devices.
That is as fundamental as one of the main advantages of receiving Wi-Fi because this connection is used everywhere. About eighty-five percent of homes today already have a Wi-Fi network, meaning interconnecting new smart devices does not require the establishment of new networks.
Cellular
Cellular protocols, such as LTE-M and NB-IoT, use existing cellular networks to provide connectivity for smart home devices. Devices equipped with a SIM card can communicate over cellular networks, offering wide coverage and reliable communication. Cellular protocols are particularly useful for smart home devices that need to operate in remote locations or areas without reliable Wi-Fi coverage.
The most advantageous aspect defining the use of cellular protocols is their data transfer capability, primarily addressing the issues with weak Wi-Fi signals. This makes them suitable for most of the IoT or smart home devices that should work in distant areas or even in conditions that are considered to be harsh.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a wired network which has high transmission speed, secure connections, and immunity to IS network interference. It is preferred for smart home appliances that need consistent and faster internet connection like smart TVs, gaming consoles, and media streaming gadgets.
At the same time one of the main benefits of choosing Ethernet is that each device is connected to a dedicated high-speed network. This makes it possible for devices to negotiate with each other and the internet without diffusing bandwidth or interrupting other wireless devices.
Comparison of Smart Home Communication Protocols
| Communication Protocol | Benefits | Limitations | Security | Typical Use Cases |
| Ethernet | High speed, reliable, low latency | Requires wired infrastructure | Secure when properly configured | Smart TVs, media streamers, NAS devices |
| Wi-Fi | High bandwidth, widely adopted, no distance limitations | High power consumption, interference issues | WPA2/WPA3 encryption, vulnerable to hacking if not secured properly | Smart TVs, cameras, voice assistants |
| Bluetooth/BLE | Low power, secure connections, widely adopted | Short range, limited bandwidth | Encryption and authentication protocols | Wearables, health monitors, smartphone-connected devices |
| Z-Wave | Low power, reliable mesh network, good range | Limited bandwidth, proprietary standard | AES-128 encryption, secure pairing | Home automation, sensors, lighting, door locks |
| Zigbee | Low power, mesh network, open standard | Limited bandwidth, potential interference | AES-128 encryption, secure joining | Home automation, sensors, lighting, thermostats |
| Matter | Interoperability, secure, IP-based | New protocol, adoption still ongoing | Encryption, authentication, access control | Home automation, voice assistant integration |
| RBF | Low power, long range, proprietary | Limited to Roombanker devices | Proprietary encryption | Roombanker smart home devices |
| Sub-GHz (LoRa, etc.) | Long range, low power, good penetration | Low bandwidth, potential interference | Encryption and authentication protocols depend on specific implementation | Environmental sensors, security devices, smart city applications |
| Cellular | Wide coverage, reliable connection | High power consumption, data costs | Cellular network encryption and authentication | Outdoor security cameras, remote monitoring devices |
What to Consider When Choosing Smart Home Wireless Protocols
When selecting a smart home wireless protocol, there are several key factors to consider:
Range
Distance refers to the distance over which several devices are capable of communicating to each other based on the wireless protocol. They also stated that situation in some European countries like Portugal poses some challenges due to thick walls in the houses. Specifically, in such instances are likely to be popularized protocols that manage to penetrate through the walls well, such as Z-Wave. Thus, for instance, if the houses are large and the utilization of the protocols for long range is possible, Middle Eastern facilities may benefit from employing the LoRa or sub-GHz protocols.
Power Consumption
The energy demands are also an essential aspect of each gadget, especially those that operate from a battery source. Bluetooth Low Energy and Zigbee are suitable for apps that require power efficiency as some gadgets are only expected to transmit data infrequently for instance in temperature and humidity monitor apps or smoke detectors. Hence, for devices that need to be in use all the time or for those that need to support high bandwidth such as video doorbells, Wi-Fi would to be preferred despite the increased power consumption.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth can in simple terms be defined as the capacity of a network to allow data transfers within a given time. Real-time applications that involve large amounts of data like streaming of videos or audios often are dependent on protocols like Wi-Fi or Ethernet, and larger bandwidth. Simple devices that only require small amounts of data (such as a sensor or switch) do not require the high data rates of Wi-Fi and can be controlled using simpler protocols such as Z-Wave or Zigbee.
Cost
The overall cost of using a particular smart home protocol is easily defined by the necessary hardware and software. Some protocols, like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, are extensively used, therefore their implementation cost is low. Some may include Z-Wave and Zigbee protocols which may need additional hardware and software components and these may be slightly expensive as part of the smart home system. When selecting a protocol, it should be noteworthy that cost is always considered but should cover not only the cost of devices, hubs, and a subscription to the given protocol.
Roombanker Wholesale Smart Home Devices, OEM Rebrand Accepted!
At Roombanker, we currently have many smart home devices that support many protocols including our private protocol: RBF. Our products are highly reliable, secure, and user friendly hence the preferred choice for both small home users willing to DIY home alarm system kits. As for special requirements and preferences, you can benefit from the OEM and ODM services we provide in order to design and build the necessary smart home systems.
If you are in search of smart lights, temperature, sensors, or any other smart home products, then Roombanker is the one product you need for the job. Our professionals will discuss the different protocols used and help you choose the most suitable solution for your smart home project. To know more about our various smart home devices and solutions that can help you create the home of your desire feel free to contact us.

